|
This wiki is closed in favour of the new wiki. Information shown is likely to be very out of date. |
Difference between revisions of "Ross Planetoid"
From Discovery Wiki
Jump to navigationJump to searchm (Category added) |
m (Infocard link. Category added) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| escape_velocity = N/A | | escape_velocity = N/A | ||
}} | }} | ||
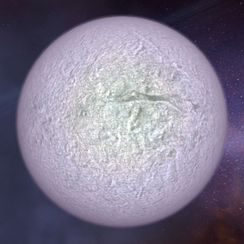
| − | Smaller than some asteroids, the Ross Planetoid exists at a gravitational sink where ice fragments have collected over the millennia and begun to compact under their own weight into the seed of what might eventually become a planet. Ross presents a unique opportunity for the [[Cambridge Research Institute]] to study planetary formation and extend their | + | Smaller than some asteroids, the Ross Planetoid exists at a gravitational sink where ice fragments have collected over the millennia and begun to compact under their own weight into the seed of what might eventually become a planet. Ross presents a unique opportunity for the [[Cambridge Research Institute]] to study planetary formation and extend their [[Terraforming]] technology. |
[[Category: Bretonia]] | [[Category: Bretonia]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Cambridge]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:54, 23 February 2019
| Ross Planetoid | |
| Location | 5F, Cambridge |
| Technical information | |
| Docking | No |
| Terrain | N/A |
| Diameter | 200 km |
| Mass | 0.66 x 10e20 kg |
| Temperature | N/A |
| Escape velocity | N/A |
Smaller than some asteroids, the Ross Planetoid exists at a gravitational sink where ice fragments have collected over the millennia and begun to compact under their own weight into the seed of what might eventually become a planet. Ross presents a unique opportunity for the Cambridge Research Institute to study planetary formation and extend their Terraforming technology.